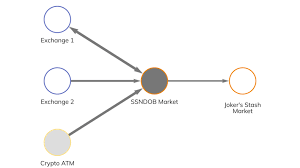
In the clandestine world of cybercrime, the marketplace for personal information is a thriving economy, where stolen identities are traded like ssndob . Among the many shadowy corners of the internet lies SSNDOB Marketplace, a notorious hub for buying and selling sensitive personal data. This underground marketplace specializes in the trade of Social Security Numbers (SSNs), Date of Birth (DOB) records, and other personally identifiable information (PII). Let’s delve into the murky depths of SSNDOB Marketplace, exploring its origins, operations, and the broader implications of its existence.
Origins and Evolution
SSNDOB Marketplace emerged in the early 2010s as a hub for cybercriminals seeking to profit from stolen personal data. Its name is derived from the common abbreviation for Social Security Number (SSN) and Date of Birth (DOB), the two primary pieces of information crucial for identity theft and fraud. The marketplace gained notoriety for its user-friendly interface, vast database of stolen information, and efficient payment systems.
Initially, SSNDOB Marketplace operated as a relatively discreet entity within the dark web, accessible only through specialized networks such as Tor. However, its reach extended beyond the confines of the dark web, with certain aspects of its operations spilling over into the broader internet.
As law enforcement agencies worldwide intensified their efforts to combat cybercrime, SSNDOB Marketplace faced significant pressure. In 2013, a series of high-profile arrests and takedowns dealt a severe blow to the marketplace, leading to its partial shutdown. However, like many Hydra-headed entities of the cyber underworld, SSNDOB Marketplace adapted and reemerged in various forms, often under different aliases and iterations.
Operations and Offerings
At its peak, SSNDOB Marketplace operated as a one-stop shop for personal information, offering a wide array of data packages for sale. These packages typically included SSNs, DOBs, addresses, phone numbers, and other sensitive details. The marketplace catered to a diverse clientele, including identity thieves, fraudsters, and individuals involved in various forms of cybercrime.
The process of purchasing data on SSNDOB Marketplace was remarkably straightforward, resembling a typical e-commerce transaction. Buyers could browse through listings, select desired data packages, and complete transactions using cryptocurrency, ensuring a degree of anonymity for both buyers and sellers.
To maintain the quality and relevance of its offerings, SSNDOB Marketplace employed various techniques to verify the authenticity of the data. This included cross-referencing information from multiple sources, such as data breaches, phishing attacks, and social engineering tactics.
Implications and Countermeasures
The existence of SSNDOB Marketplace and similar platforms poses significant challenges for individuals, businesses, and law enforcement agencies alike. The widespread availability of personal data fuels a myriad of illicit activities, including identity theft, financial fraud, and cyberattacks.
For individuals, the risk of identity theft looms large, as their sensitive information becomes increasingly accessible to malicious actors. The consequences of identity theft can be devastating, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage and legal complications.
Businesses also face substantial risks in the wake of data breaches and information leaks. The exposure of customer data not only erodes trust and credibility but also exposes organizations to regulatory penalties and legal liabilities. Moreover, the proliferation of stolen data fuels a thriving black market for cybercriminals, perpetuating a cycle of illicit activity and economic harm.
In response to the growing threat posed by SSNDOB Marketplace and similar platforms, efforts to combat cybercrime have intensified on multiple fronts. Law enforcement agencies have stepped up their efforts to identify and dismantle these illicit marketplaces, often collaborating with international partners and cybersecurity experts.
Furthermore, businesses and individuals are increasingly adopting proactive measures to safeguard their data and mitigate the risk of compromise. This includes implementing robust cybersecurity protocols, employing encryption technologies, and fostering a culture of cyber hygiene and awareness.
Conclusion
SSNDOB Marketplace stands as a stark reminder of the pervasive threat posed by cybercrime in the digital age. As long as there exists a demand for stolen personal data, illicit marketplaces like SSNDOB will continue to thrive, perpetuating a cycle of exploitation and vulnerability.
Addressing this multifaceted challenge requires a concerted effort from governments, law enforcement agencies, businesses, and individuals alike. By enhancing cybersecurity measures, fostering greater collaboration, and raising awareness about the risks of data exposure, we can collectively combat the scourge of cybercrime and safeguard the integrity of our digital ecosystem.